It’s often touted that Google’s search algorithm uses more than 200 factors to determine rankings.
But how does Google determine which website to rank on page one? For us it can be simplified to two important factors. On-page and off-page. If you get the on-page right, then build quality links to the page, it will rank.
In fact, a recent study of over 1 billion pages by Ahrefs found that pages with more links rank higher.
SEO fact: Pages with more backlinks tend to rank higher in SERPs.
In our study of 1 billion pages, we found a strong positive correlation between the number of websites linking to a page, and how much search traffic that page gets from Google.
Link building is important 🔥 pic.twitter.com/twWjF1gTWr
— Ahrefs (@ahrefs) March 21, 2022
Link building is a different skillset in SEO though. And an awkward truth is that many SEOs don’t like to build links. In fact many of them straight up hate it and will do whatever they can to avoid building links.
That’s why many SEO agencies don’t include link building in their retainers as standard. They either don’t want to or don’t know how to build links.
Especially the high quality links you need to outrank your competition.
This can be your advantage, if you can build more high quality links than your competitor. You’ll be able to outrank them.
In our guide to link building we’re going to teach you how to build high quality links that your competitors can’t.
You’ll learn:
- What is link building?
- How to build backlinks
- What makes a great link
- Link Authority
- Linkable Assets
- Broken link building
- How To Scale Your Link Building Campaign
What is link building?
Link building is the process of getting other websites to link to a page on your website with the goal of increasing your rankings and website traffic.
Generally speaking, the more high quality links your website has, the higher your website will rank.
The easiest way to understand the impact of a link, is that search engines see each link from another website as a vote that your content is valuable and relevant.
The relevance of a link is based on the content of the linking page/site.
That’s why it’s important to search for sites that talk about the same subject, or that is in the same niche as your site.
Here’s a simple example, if your website was about landscape gardening, a link from another website/webpage that talks about landscape gardening is a highly relevant link.
How to build backlinks
So what are the three main types of link building strategies? Loosely speaking, there are three types:
1. Submission type links: Submission links are links you can get by submitting your website to another website. This can be done by adding your website to social media profiles, directories or leaving meaningful comments on blogs or forums such as Reddit and Quora.
Because these links tend to be easier to get, these are considered low quality links and in most cases they won’t significantly move the needle.
2. Buying links: This is the elephant in the room. It is 100% against Google’s guidelines and it can negatively impact your site’s ranking in search results. However, that’s not to say it doesn’t work. Many SEO’s have had a ton of success by buying links. Private Blog Networks are one of the most popular ways to buy links.
Sites like Fiverr, Legit, the Warrior Forum and Reddit are popular places to buy links. Buying links is a black hat strategy though and isn’t a strategy we use or one that we implement for our clients because we prefer to use “White-hat strategies”
3. Earning links: The number one way to earn links is to create an amazing piece of content known as a “link magnet” or a “linkable asset”, then reaching out to website owners and authors in relevant niches and asking them to link to it.
This is the best strategy to build links in my opinion and this link building guide will show you a number of tactics you can use to build these links.
The anatomy of a great link
Not all links are created equal! Some will help propel your pages to the top of Google, while others can hurt your site.
What makes a high-quality backlink?
There are two main categories to look out for.
The Relevance Of The Link
Ideally, you want to get backlinks from relevant websites and pages.
Let’s imagine you have created a piece of content on the ‘best kitchen cabinet paint colours’ (Like this one, from Improovy). Getting a link from a page on the topic of interior design would be much more relevant than a link from a page about fitness tips.
Ideally, you want to get links that are relevant to the story you’re writing.
There are a number of different factors in the strength of a link:
- Destination URL: This is the URL address of the page the person will reach when the link is clicked
- Anchor Text: This is the clickable word/phrase/image attached to the link. It’s often blue and underlined.
- Rel Attribute: This defines the relationship between the page a link is on and the page it is pointing to. There are three rel values you should be aware of.
Rel Attributes
- No-Follow Link: This tells search engines not to crawl/follow the outbound link. It essentially means that the website linking to you is not “voting” for you. As a result, it will not pass SEO ranking power.
Many publications now add the nofollow tag to outbound links. Here’s what a nofollow links looks like in the code:
<a href=”https://example.com” rel=”nofollow”>Anchor Text</a>
You can quickly identify Follow/No Follow links through the NoFollow plugin.
Once you’ve installed the plugin. If a link is outlined in red, it is a “No Follow” link.
When you’re analysing a website for Follow/No Follow links just look at the main body of text, don’t look at links on the page like those which link out social media websites or the author biography.

UGC: This stands for User Generated Content, and the UGC value is recommended for comments and forum posts. UGC link can be identified as follows:
<a href=”https://www.example.com/” rel=”ugc”>Anchor Text</a>
- Sponsored: This tag identifies links that were paid for. Use the sponsored value to identify links on your site that were created as part of advertisements, sponsorships or other compensation agreements. The sponsored link can be identified as follows:
<a href=”https://www.example.com/” rel=”sponsored”>Anchor Text</a>
The Authority Of A Link
Google’s original algorithm contained something known as Pagerank. In fact, the reason Google’s algorithm was so much better than their competitors is largely because of page rank.
In the early days, Google even had a tool where they would tell you what your pagerank was.
But because SEO’s got so good and realized if they could get a higher page rank, they would rank higher, Google no longer makes pagerank public.
It’s not known if Pagerank is still part of the algorithm, however it is strongly believed that it is.
If Pagerank is no longer part of the algorithm, it is believed that it has been replaced by something newer and more sophisticated, but based on the same principles that Pagerank was built on.
The weight of Pagerank in the algorithm is often referred to as “Authority” when it comes to SEO.
The authority of a website or a web page linking to your own website is a ranking factor.
If you have more, high quality links from a more authoritative site than your competitors, you will likely outrank them.
Many SEO tools have tried to create their own version of Pagerank to interpret the authority of a page.
Moz uses Domain Authority (DA) for instance, Ahrefs has created Domain- Rating (DR) and Majestic SEO has created Trust Flow.
To check a website’s authority using Majestic SEO’s Trustflow metric, you can download the Majestic plugin.
Majestic gives us information about the links that are pointing to that given page/website.
When you’re analyzing any website focus on the following four attributes:
- URL
- Root Domain
- Trust Flow
- Referring Domains
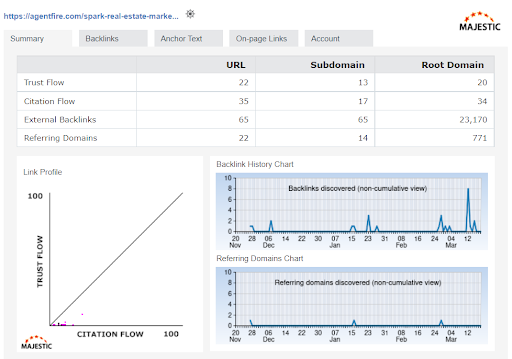
URL: This tells us about the specific page we are on. So, in this case, we are on the “Spark Real Estate Marketing” page. The URL is showing us all the links pointing to that page.
Root Domain: Analyzes the links that are pointing to the entire website. This adds up all the links, for example, the About Us Page, Blog Page, Contact Us Page etc.
Trust Flow: This is the overall quality of the links pointing to the page/domain. The higher the score the better. Any trust flow over 15/20 it’s considered a high-quality site.
Referring Domains: This is the total number of links pointing to the page/domain.
Linkable Assets
When it comes to link building it might seem that it’s all technical jargon but there’s also a creative aspect that’s required.
Link building is about value, you need to find out what value you can offer with your content as well as get creative with your email pitch.
First and foremost create content that is worth linking to. This is what we call a “Linkable asset”. A linkable asset is any piece of content with a high probability of acquiring backlinks.
So, what are the benefits of creating a linkable asset?
Linkable content can increase your referral traffic as you’re getting links from other authoritative websites in your niche.
Linkable assets will also lead to increased brand exposure, as journalists and industry-leading blogs will cite your content in their articles.
There are a number of linkable asset formats you can create:
- Case Studies
- Original Research/Studies
- Infographics
- List Posts
- Free Tools
- Research Using Trends and Statistics
Let’s explore some of these in more detail:
1. Infographic
An infographic is a great way to use visuals to showcase your findings.
If choose to create an infographic as your linkable asset, pick one topic that appeals to websites in your niche. Brian Dean refers to these people as “Linkreators” – people who run websites in your industry or a related industry.
Try to brainstorm – What topics are they passionate about? What topics are they arguing against? Let’s imagine your linkeators are running bloggers. And you notice that a good chunk of these linkreators don’t recommend running every day to reach your goals.
You’d want to make an infographic topic that they agree with, EG something like: “Why too much running is bad for your health”.
Make sure in your infographic you cover 6/10 data points.
If you feel stuck with your ideas check out visual.ly to find infographics in your space or Google “topic” + “infographic”.
If you don’t have design skills don’t worry you can hire a graphic designer on websites such as Fiverr. So, don’t sweat the small stuff.
2. Original Research/Studies
Original studies naturally attract links. Why? They offer unique data and insights on a winning topic.
In order to get coverage, you need to have something interesting to write about.
How to choose your topic? Use the Source Magnet Technique (Another Brian Dean creation).
- Is this topic trending?
- Does this topic lack data?
- Is your topic a “Tangential Topic”? (Topic that is related but not directly about your business)
In order to find what’s trending, put your topic into Exploding Topics or Google Trends.
Remember journalists want something that is blowing up. Once you have chosen your topic, collect and analyze your data.
If you’re doing a DIY Industry Study you should have a sample of at least 1,000 of whatever it is you’re looking at. Trim your list down to 12/15 data points. Important note: Journalists want to see how you conducted your study.
When you’re organizing your results, start off with the most compelling finding to grab the reader’s attention.
If you want to promote your study even further find influential people in your space that cover some of the topics that your study is about.
Reach out to them and ask them to give their thoughts about one specific topic they’re most interested in.
This will add credibility to the content. Once it’s published, share your content with those influential people.
They are more likely to share your content as they contributed their expertise and it will make them look good.
Content frameworks for linkable assets
There are 7 content frameworks that are ideal to create linkable assets with.
1. Trademark Technique: Identify a problem a linkreator and their audience cares about.
Follow these simple steps:
- Choose a Catchy Headline: The title is the first thing a potential reader sees and getting it right is the single most important thing.
In your headline use three of the following:
1. A specific result
2. Specific Number (this increases credibility)
3. Specific Timeline (days/weeks are much better than months/years)
For example, How to (Achieve a Specific Result) in Only (Timeframe).
- Identify Obstacles: Pick one obstacle that stands between someone and their solution. Give a brief overview of the obstacle and outline specific results in the Introduction. Share a solution that hasn’t been seen before and combine it with a unique name so it sticks in people’s minds.
- Branded Solution Elements: The solution needs to be descriptive and must contain a visual element. Combine your branded solution with one of these terms: Approach/Formula/Method/System/Technique.
- The First Section: Don’t jump into the steps of your branded solution. List out your results the following way:
1. Result #1 – Branded solution name & the Benefit you got from your solution
2. Result #2
3. Result #3
- The Details:
1. Include 3/5 very detailed steps.
2. Show people how to implement each step exactly
- Write your Content as a Case Study: It’s important to show actual proof. Try to avoid the “this changed my life” type commentary. Average type results will do as they are more believable and attainable.
- Conclusion:
1. Make a Brief Summary of your findings.
2. Make sure to include Call to Action.

2. Go-to-Guidebook: Contains just about everything someone needs to know about a specific topic.
Steps to follow:
Choose a broad topic that can be broken down into 7/10 sub-topics which is not too broad or too narrow.
Use Google Trends/Buzzsumo for topics that have already proven to perform well in your industry.
One you have your idea organise it into chapters:
- Beginning: Basic/Introductory Topics
- Middle: Detailed and Advanced Topics
- End: Short Case Studies/Brief Tutorials/Tips etc.
Add Table of Contents and list out all your chapters and add page jump links.
For each chapter first write a short intro. This should briefly describe why this sub-topic is important. Then briefly describe 3-5 things someone needs to know about the subtopic.
Conclusion: Ask your readers to comment – you want them to take action once they’re done reading.

3. Expanded List Post: These articles contain a list of tips and tricks readers can use to achieve specific results. The list should be brief and easily digestible. Avoid writing in-depth paragraphs.
Steps to Follow:
- Find a topic that you can provide 17/27 bite-sized tips on.
- If you’re stuck, research other blogs using keywords like “your topic” + tips and “your topic” + strategies. You want techniques and tactics that people can use that day.
- Do keyword research to figure out what people are already searching for. If you search for a keyword and no list posts show up this means it’s it isn’t a good for for a list post.
- Find 3/4 best tips for each technique. You can include actionable steps, screenshots, video tutorials, infographics and extra content to beef up your content. Tell them exactly what to do.
- Conclusion: You want people to take action.

4. Ego Bait: Make your topic linkreator friendly meaning a topic that journalists will be willing to link to.
Steps to Follow:
- Your topic needs to be: specific and in a niche with at least 100 other blogs.
The 100 blogs benchmark to see whether a topic is the right size.
- Gather your list of winners. Make sure the blogs you choose cover the topic now and again. Include at least 25 winners in your AwardsBait campaign. The more sites you include the more links you’ll get.
- Use .edu sites as they are authoritative. To find them simply search: site: edu + fitness blog. Use Alltop.com for linkreator research. Type in the keyword that describes your AwardsBait topic. Use best of lists to find more potential bloggers.
- Choose your blogs and narrow the finalists down to 25-100.
- Create AwardsBait Power Page by choosing a good title for example, “Top 50…” and add your keyword after so people know what your page is about.
- Don’t put your winners in any particular order in this case “everyone is a winner” BUT put the most authoritative and popular sites at the top.
- Create a listing for each winner. Include the following four elements in the listing: their name/blog’s name, a flattering bio, an image and link to their site or social media profile.
- Promote your piece using unique logo/banner, create a badge for your winners and reach out to your winners.Write an intro using this formula:Introduce what the awards are, talk about how many blogs exist in this niche, emphasize that it’s an exclusive list and outline what your blog will bring to the table.
5. The Industry Study: Is a great way to show off your market research about a certain topic.
You can review the links your competitor has, then build a list of websites to reach out to and ask them if they will also include your website.
Broken Link Building
Broken link building is a process where you look for your pages that are similar to yours that have gathered some links, but the website is now offline so they are broken (404).
Here’s an example of a 404 page:
If you can find a broken page in your niche, then you can use Ahrefs to look at the websites that link to that broken page.
Then you can reach out to the sites that link to the broken page and let them know they have a broken page, but it’s OK because you’ve got a similar piece of content they can link to instead.
In your outreach email tell your designated contact exactly where the broken link is and provide your content as a solution.
Guest Posts
Guest posting will increase your credibility and increase your brand awareness. If you can include a link to your website within the content or at the end in the author bio, it can still be a great link building strategy.
This process takes time as you have to find websites that still accept guest posts and figure out a unique topics to write about.
Link Roundups
Link roundups are ‘best of’ lists where bloggers link to their favourite articles. Here’s an example from wow group.
The key here is that you must have a quality piece of content that you have recently written. Although not as popular these days, link roundups can still be found.
Unfortunately, you can’t pitch a product/sales page. It usually has to be a blog/video/guide.
Link Reclamation
Find a website that mentions your name/brand/business but hasn’t linked to you. Then contact them to include a link to your website for the attribution process. To find unlinked mentions go to Mention.com. Ahrefs content explorer or Google Alerts.
Resource Page Link Building
A resource page Is a blog post/dedicated page that links out to that individual’s favourite things they think their audience will find helpful. You can create content around that link and pitch it to other potential resource pages.
For example if your website was a website that offered free stock photos, you would find resource pages that had a list of free stock photos.
Sponsored Posts
For sponsored posts, you’re looking for sites that actively accept advertisements. When evaluating the quality of sponsored posts look for:
- Overall domain authority and trust flow
- Content quality (are there any spamming links?)
- Sponsored posts (do they say “sponsored post”?)
Digital PR
Digital PR is our favourite way to build links at Legacy Communications. Digital PR involves creating a story that news websites and journalists will love and will publish, ideally with a link to your linkable asset. You can get the full play-by-play in this Digital PR case study.
If you’re interested in our Digital PR services for link building, you can also reach out to us directly, we’d love to chat!
How To Scale Your Link Building Campaign
There are a number of ways you can scale your link building campaigns and in this section we’re going to take you through them.
Create separate link building roles
At Legacy, we favour the link building process created by Ryan Stewart at Webris.
In this process, the link building team is separated into 4 clear roles:
The Link Prospector – This person spends time looking for relevant websites to pitch and collects email addresses for the right contacts.
The Outreach Manager – This is the person who spends their time reaching out to new websites, promoting linkable assets and ultimately asking them for a link
The Content Writer – When the outreach manager gets a pitch accepted for a guest post, they forward the content brief to the writer, who then spends the time to write the post
The Lead SEO – This is the SEO who sets the target pages for links, as well as setting the full SEO strategy.
Use Outreach Tools To Build Links At Scale
There are a number of tools you can use to build links at scale. These tools will help by automating pitch emails, automatically sending follow ups and more.
There are a number of tools that are popular with link building teams around the world:
-Mailshake
-Pitchbox
-Buzzsumo
-Ninja Outreach
-Just Reach Out
-Press Hunt
Link Building Guide: Conclusion
The digital space is constantly evolving. If you can’t adapt your business will be left behind.
Always remember that link building is about exchanging value.
If your content is not link-worthy, then don’t expect other sites to link to it.
Your content is your biggest asset when it comes to link building campaigns so use it to your advantage to increase organic traffic for your business.

